The GBP to USD exchange rate, representing the value of the British pound (GBP) against the US dollar (USD), is a critical economic indicator closely watched by businesses, investors, and individuals worldwide. This rate reflects the relative strength of the two economies and is constantly in flux due to a complex interplay of factors. Understanding how this exchange rate works, what influences it, and its implications is crucial in today’s interconnected global marketplace. This article provides a comprehensive guide to the GBP to USD exchange rate, exploring its history, the forces that drive its movements, and the practical consequences for various stakeholders.
A Historical Perspective: GBP and USD
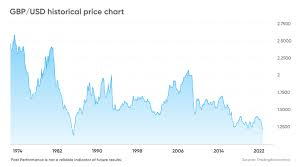
The British pound sterling, with its rich history spanning centuries, is one of the world’s oldest currencies. The US dollar, while relatively younger, has become the dominant global reserve currency. Their relationship has been dynamic, mirroring the shifting economic and political landscape.
The Bretton Woods agreement after World War II established a fixed exchange rate system, pegging the pound to the dollar. However, this system eventually collapsed, giving way to the floating exchange rate regime we operate under today. In this system, the pound’s value against the dollar is determined by market forces, primarily supply and demand. This means the rate is constantly adjusting, sometimes dramatically, based on a multitude of influencing factors.
Decoding the Dynamics: Factors Influencing GBP to USD
Numerous factors contribute to the fluctuations of the GBP to USD exchange rate. These can be categorized as:
Economic Factors
Interest Rates: Interest rate differentials between the UK and the US are a key driver. Higher interest rates in the US, for example, can attract foreign investment, increasing demand for the dollar and potentially weakening the pound. Conversely, higher UK interest rates could strengthen the pound.
Economic Growth: Strong economic growth in the US relative to the UK can bolster confidence in the dollar, leading to appreciation against the pound. Conversely, robust UK growth can strengthen the pound.
Inflation: Inflation rates in both countries are crucial. Higher inflation in the UK compared to the US can weaken the pound as its purchasing power decreases. The opposite holds true if US inflation is higher.
Trade Balances: The trade balance between the two countries (the difference between exports and imports) can also impact the exchange rate. A trade surplus for the US (more exports than imports) can strengthen the dollar, while a trade deficit can weaken it. From the UK perspective, a trade surplus would strengthen the pound.
Political Factors
Political Stability: Political uncertainty or instability in either country can significantly impact the exchange rate. Events like elections, referendums (e.g., Brexit), changes in government, or political crises can create volatility and influence investor sentiment.
Government Policies: Government policies, such as fiscal stimulus, tax changes, or trade agreements, can have a direct or indirect impact on the value of their respective currencies.
Global Factors
Global Economic Conditions: Global economic growth or recession can influence investor sentiment and risk appetite, affecting currency valuations. During times of global uncertainty, investors often seek safe-haven currencies like the US dollar, increasing demand and strengthening it.
Geopolitical Events: Major geopolitical events, such as international conflicts, terrorist attacks, or global pandemics, can create significant volatility in currency markets. These events can shift investor sentiment and lead to rapid fluctuations in exchange rates.
Market Speculation: Currency traders and speculators can also influence exchange rates through their buying and selling activities. Large trades can sometimes trigger significant price movements, especially in the short term.
The Mechanics: How the GBP to USD Exchange Rate Works
The GBP to USD exchange rate is quoted as the amount of US dollars one British pound can buy. For example, if the exchange rate is 1.25, it means one pound can be exchanged for 1.25 US dollars. This is the inverse of the USD to GBP rate.
The exchange rate is determined in the foreign exchange market, a decentralized global marketplace where currencies are traded. Participants include banks, financial institutions, corporations, and individual traders. The market operates 24 hours a day, five days a week, with trading centers located around the world.
Real-World Implications: Impact on Various Stakeholders
The GBP to USD exchange rate has significant implications for various stakeholders:
Businesses
Importers and Exporters: Businesses that import goods from the US and pay in dollars are affected by the exchange rate. A stronger dollar makes imports more expensive in pound terms. Exporters to the US receive more pounds when the dollar is strong. Conversely, a stronger pound makes US imports cheaper for UK businesses.
Multinational Companies: Companies with operations in both the US and the UK need to manage currency risk, as fluctuations in the exchange rate can impact their profits and financial statements.
Individuals
Travelers: Tourists traveling to the US will find their expenses higher when the dollar is strong and lower when it is weak. The same applies to US tourists visiting the UK.
Investors: Investors holding assets in either currency are exposed to exchange rate risk. Changes in the rate can impact the value of their investments when converted back to their home currency.
Remittances: Individuals sending money to or receiving money from the US or the UK are also impacted by the exchange rate.
Governments and Central Banks
Monetary Policy: Central banks, like the Bank of England in the UK and the Federal Reserve in the US, consider the exchange rate when making monetary policy decisions.
International Trade: Governments monitor the exchange rate as it can affect their country’s competitiveness in international trade.
Navigating the Fluctuations: Understanding and Managing Risk
Exchange rates can fluctuate significantly and unpredictably. While perfect prediction is impossible, understanding the influencing factors can help businesses and individuals make informed decisions.
Monitoring Economic Indicators: Tracking key economic indicators, such as interest rates, inflation, and economic growth figures, provides insights into potential exchange rate movements.
Staying Informed about Political Developments: Following political events and policy changes in both the US and the UK is essential, as these can create uncertainty and impact the currency markets.
Using Financial Tools: Various financial tools, such as forward contracts and options, can help businesses and investors hedge against exchange rate risk.
Seeking Professional Advice: Consulting with financial advisors or currency specialists can be beneficial for individuals and businesses seeking guidance on managing exchange rate risk.
The Digital Age: Accessing and Analyzing Exchange Rate Information
The internet has made it easier than ever to track the GBP to USD exchange rate. Numerous websites and mobile apps offer real-time exchange rate quotes, historical data, and analysis. This accessibility of information empowers individuals and businesses to make more informed decisions about currency exchange.
Social media can also be a source of information and discussion about exchange rates. However, caution is advised when relying solely on social media for financial information, as accuracy and reliability can vary.
FAQs
What does the GBP to USD exchange rate mean?
The GBP to USD exchange rate represents the value of the British pound (GBP) in relation to the US dollar (USD). It tells you how many US dollars are needed to purchase one British pound. For example, if the GBP/USD rate is 1.30, it means one British pound can be exchanged for 1.30 US dollars. This rate is constantly fluctuating based on various economic and political factors.
How is the GBP to USD exchange rate determined?
The GBP to USD exchange rate is primarily determined by the forces of supply and demand in the foreign exchange market. This is a decentralized global marketplace where currencies are traded 24 hours a day, five days a week. If demand for the pound increases relative to the dollar, the pound’s value will likely rise, and the GBP/USD rate will increase (meaning you get more dollars for each pound). Conversely, if demand for the dollar increases, the rate will likely decrease.
What factors influence the GBP to USD exchange rate?
Several key factors influence the GBP to USD exchange rate:
Interest Rates: Differences in interest rates between the UK and the US can attract or deter foreign investment, impacting currency demand. Higher US interest rates, for example, can strengthen the dollar and weaken the pound.
Economic Growth: Strong economic performance in one country relative to the other can boost confidence in its currency. Stronger US growth can strengthen the dollar against the pound.
Inflation: Higher inflation in one country can weaken its currency as its purchasing power decreases. Higher UK inflation relative to the US could weaken the pound.
Trade Balances: A trade surplus (more exports than imports) can strengthen a currency, while a trade deficit can weaken it.
Political Stability: Political uncertainty or instability in either country can create volatility and weaken its currency. Events like elections or referendums can have a significant impact.
Global Economic Conditions: Global economic growth or recession, and associated risk appetite, can influence currency valuations. During times of uncertainty, investors often flock to the US dollar as a safe haven.
Geopolitical Events: International conflicts, crises, or pandemics can cause significant fluctuations in exchange rates.
Market Speculation: Large trades and speculative activity can also influence short-term price movements.
Where can I find the current GBP to USD exchange rate?
You can easily find the current GBP to USD exchange rate on numerous financial websites, currency converter tools, and even through a simple Google search. Reliable sources include major financial news outlets, central bank websites (like the Bank of England and the Federal Reserve), and dedicated currency trading platforms.
How does the GBP to USD exchange rate affect me?
The exchange rate can impact you in several ways:
Travel: A strong dollar makes travel to the UK more expensive for Americans, while a strong pound makes travel to the US more expensive for Britons.
Shopping: If you buy goods from the US, a strong dollar means you’ll pay more in pounds. The opposite is true for UK goods purchased in dollars when the pound is strong.
Investments: If you invest in US assets, a strong dollar increases their value when converted back to pounds. The opposite is true for UK investments when the pound is strong.
Remittances: The exchange rate affects the amount of money you receive when sending or receiving money between the US and the UK.
In Summary
The GBP to USD exchange rate is a vital economic indicator with far-reaching consequences. Understanding the complex interplay of factors that influence it, from interest rates and inflation to political events and global economic conditions, is crucial for businesses, individuals, and investors alike. While predicting currency movements with precision is extremely challenging, staying informed, utilizing available financial tools, and seeking professional advice can help navigate the intricacies of the foreign exchange market.
The wealth of online resources, from real-time exchange rate updates to expert analysis, empowers individuals to make well-informed decisions about currency exchange and manage their exposure to the inevitable fluctuations. Recognizing the dynamic nature of the exchange rate and its potential impact on various aspects of life and business is key to sound financial planning in our increasingly interconnected world.
To read more, Click here.